POTELIGEO helped slow the spread of Mycosis Fungoides (MF) or Sézary Syndrome (SS)
When talking about POTELIGEO, your doctor may say:
Progression-free survival (PFS)
Which means:
How well treatment prevented Mycosis Fungoides (MF) or Sézary Syndrome (SS) from spreading further
- POTELIGEO was shown to slow the spread of Mycosis Fungoides (MF) or Sézary Syndrome (SS) on the skin and in the blood
- POTELIGEO stopped disease from worsening for more than 2 times as long as those not on POTELIGEO
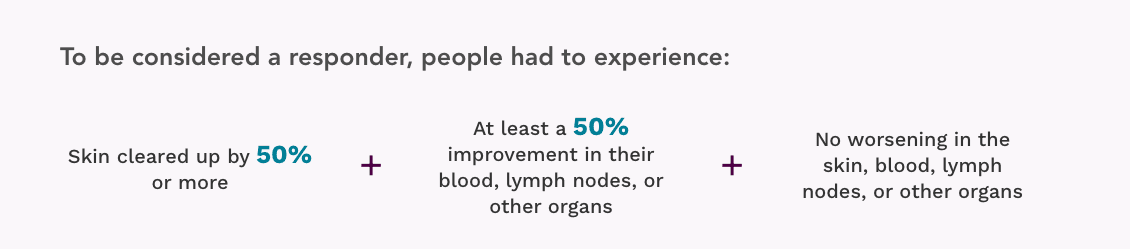
More people responded to treatment with POTELIGEO
When talking about POTELIGEO, your doctor may say:
Overall response rate (ORR)
Which means:
How well Mycosis Fungoides (MF) or Sézary Syndrome (SS) responded to treatment in areas of the body where disease was found when entering the trial
More than 5 times as many people (28%) were classified as responders to treatment with POTELIGEO than with vorinostat (5%)
Response in skin
More than 2 times as many people on POTELIGEO
saw their skin improve
POTELIGEO
0 %
RESPONDED
VS
vorinostat
0 %
RESPONDED
Response in blood
Nearly 4 times as many people on POTELIGEO saw
a lower cancerous T-cell count in their blood
POTELIGEO
0 %
RESPONDED
VS
vorinostat
0 %
RESPONDED
People responded faster to POTELIGEO
When talking about POTELIGEO, your doctor may say:
Time to response (TTR)
Which means:
How long it took people to respond to treatment
Overall, people who responded to treatment with POTELIGEO did
so almost
2 months faster than those treated with vorinostat
2 months faster

- People treated with POTELIGEO saw a median response in blood in 1.1 months and response in skin in 3.0 months
POTELIGEO worked longer than vorinostat
When talking about POTELIGEO, your doctor may say:
Duration of response (DoR)
Which means:
How long people responded to treatment